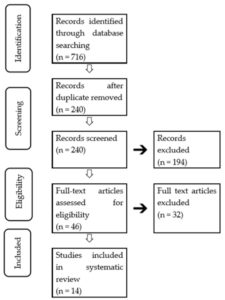
Vitamin C is important for preventing and slowing the progression of many diseases. There is significant evidence linking periodontal disease and vitamin C. We aimed to systematically review the studies addressing the relationship between vitamin C and periodontal disease, and the preventive ability of vitamin C against periodontal disease. Electric searches were performed using PubMed, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, and Web of Science. Studies addressing the relationships between periodontal disease and vitamin C in adults aged over 18 years were included. Quality assessment was done using the Critical Appraisal Skills Program guideline and GRADE-CERQual. There were 716 articles that were retrieved and 14 articles (seven cross-sectional studies, two case-control studies, two cohort studies, and three randomized controlled trials (RCT)) were selected after reviewing all of the articles. The vitamin C intake and blood levels were negatively related to periodontal disease in all seven cross-sectional studies. The subjects who suffer from periodontitis presented a lower vitamin C intake and lower blood-vitamin C levels than the subjects without periodontal disease in the two case-control studies. The patients with a lower dietary intake or lower blood level of vitamin C showed a greater progression of periodontal disease than the controls. The intervention using vitamin C administration improved gingival bleeding in gingivitis, but not in periodontitis. Alveolar bone absorption was also not improved. The present systematic review suggested that vitamin C contributes to a reduced risk of periodontal disease.
Affiliations
- 1Department of Health Science, Hyogo University, 2301 Shinzaike Hiraoka-cho, Kakogawa, Hyogo 675-0195, Japan. atada@hyogo-dai.ac.jp.
- 2Department of International Health and Collaboration, National Institute of Public Health, 2-3-6, Minami, Wako, Saitama 351-0197, Japan.